Market Access Map (MAcMap) is a free analytical portal that allows users to access, compare, analyse and download customs tariffs, tariff rate quotas, trade remedies and non-tariff measures applicable to a specific good in any market in the world. The web application is interactive, simple and easy to use.
Thanks to financial contributions from the European Commission, GRIPS and donors to ITC's trust fund, users in developing countries and territories can register to access ITC's Market Analysis Tools free of charge. By registering, users in developed countries can obtain free access to a large part of ITC's Market Analysis Tools. However, developed country users must subscribe to gain full access to these tools. See subscription options and fees.
The reasons can be the following:
If you still cannot access MAcMap, please contact us at marketanalysis@intracen.org and provide us with the following information:
Note on web browser compatibility: MAcMap is optimized for desktop devices with modern web browsers including Chrome, Firefox and Edge. MAcMap may not function optimally on Safari.
MAcMap data are continuously updated since 1996. For a given country, the update occurs once a year, whenever possible. However, some countries may change their tariff rates and/or market requirements several times a year. Although we do not always capture those changes, we do our best to publish the most up-to-date information. In MAcMap, the year of data update is indicated for each type of data. To learn more about MAcMap data per country, please consult the Data Availability submodule.
Since 2005, ITC's MAcMap team has been collecting the customs tariffs and taxation data directly from trusted national focal points who provide the national legislations applied by the institutions in each country. Applied tariff data include general, most-favoured-nation (MFN), preferential tariff rates and tariff rate quotas.
Final bound rates come from the WTO's Consolidated Tariff Schedule (CTS) database.
Non-tariff measures (NTMs) are collected jointly with UNCTAD and the World Bank.
Trade remedies data are based on official legislations published by national institutions and notifications of these measures to the WTO.
Trade data is sourced from ITC's Trade Map database.
Not entirely. The table below summarizes the differences in trade data between the two applications:
| Web application | Market Access Map | Trade Map | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of the database | Normalized trade matrix | Trade Map and UN COMTRADE | Trade Map |
| Time series | From 2005 | 1996-2005 | From 2001 |
| Frequency | Yearly | Yearly | Yearly, quarterly, monthly |
| Variables | Values | Values | Values and quantities |
| Type of data | Direct and mirror data | Direct data | Direct and mirror data |
| HS revisions | All HS revisions | Native revisions (as reported by the country) | Native revisions (for trade data); HS revision 2012 (for indicators) |
| Deepest disaggregation level | Internationally harmonised HS 6-digit level | Internationally harmonised HS 6-digit level | National Tariff Line (8-digit levels or more) |
Due to conversion of HS revisions and the presence of mirror data, the values obtained using MAcMap may diverge from the ones retrieved from Trade Map application.
The Harmonized System (HS) or the Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System is an international product nomenclature edited by the World Customs Organisation (WCO). It allows the classification of all physical goods moving across borders in a uniform manner all over the word. As of June 2018, more than 200 economies and Customs or Economic Unions use it as the basis for their customs tariffs and for the compilation of international trade statistics.
The HS comprises 5387 6-digit codes (HS revision 2017) called subheadings, which are further grouped into 1222 headings (4-digit codes), 97 chapters (2-digit codes), and 21 sections. Nonetheless, individual countries can increase the level of detail of their product classification by adding extra numbers after the HS 6-digit level code. In that case, those deeper product classifications at the country level are called National Tariff Line (NTL) and are not harmonized internationally. Additionally, their length may also differ per country (e.g. 8-, 10- or even 14-digits).
| Importing country | NTL – Product description |
|---|---|
| Viet Nam |
|
| South Africa |
|
| Argentina |
|
The Harmonized System has to be amended regularly to capture the actual situation in trade and production. The most frequent situations that trigger amendments are: change of trade volume, changing technology and products, increasing needs of monitoring for food security, health, environmental and safety reasons, and some WCO member's proposals to clarify or enhance the HS or to respond to critical national needs.
The HS revision may impact the classification codes as well as the definitions and descriptions of the legal notes, headings and subheadings.
The first general review of the HS was completed in 1993, and entered in force on January 1996. The following revisions were implemented in 2002, 2007, 2012 and 2017. More information in Product Search.
| HS Revision | Implemented in | Number of HS codes | Number of new products | Number of deleted products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 st | 1996 | 5113 | 348 | 255 |
| 2 nd | 2002 | 5224 | 338 | 227 |
| 3 rd | 2007 | 5052 | 262 | 432 |
| 4 th | 2012 | 5205 | 329 | 176 |
| 5 th | 2017 | 5387 | 263 | 81 |
Please go to Product Search. There, you can use either search by hierarchy or by key word in the product description. Keep in mind that HS product codes are unique, the descriptions may have been shortened from their original, and many products may contain the key word you searched for. Therefore, we recommend that you use the hierarchical search when possible.
When you cannot find a product with a particular HS code, the reporter country for which you are trying to select this product might be using a different HS revision. For example, from HS revision 2007 to 2012, HS6 (070990) Vegetables, fresh or chilled n.e.s. has been subdivided into: (070991) Fresh or chilled globe artichokes; (070992) Fresh or chilled olives; (070993) Fresh or chilled pumpkins, squash and gourds; and (070999) Fresh or chilled vegetables n.e.s. Therefore, you cannot select the product (070991) Fresh or chilled globe artichokes for a country that uses the HS 2007 revision.
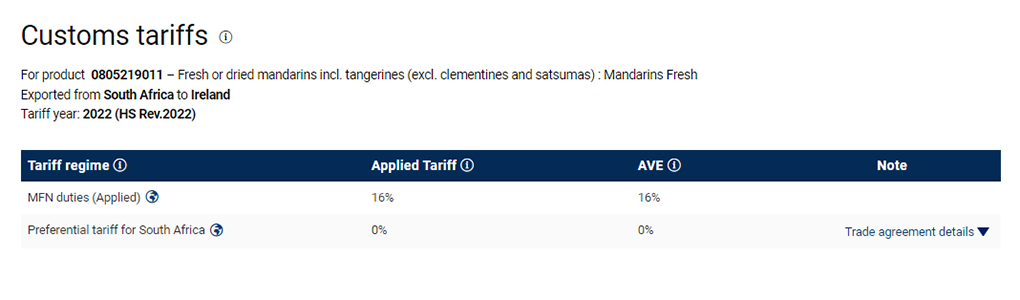
MAcMap shows you all applied tariff rates applicable to a product imported from one specific country to another. South Africa may export mandarins to Ireland at a most-favoured-nation rate of 16% or at the preferential rate of 0%. Both rates are potentially applicable, but in order for the product to qualify for a preferential rate, the product must comply with corresponding rules of origin (ROO).
An ad valorem equivalent (AVE) tariff is a non-ad valorem (NAV) tariff presented as a percentage of the value of goods cleared through customs.
AVE tariffs allow comparison across different types of NAV tariffs e.g. a tariff of $2 per unit with a tariff of 10%. They also enable the aggregation of tariff rates across products and countries.
AVEs are calculated by dividing the NAV rate by the unit value. For specific details about the methodology used in MAcMap, please visit the Methodology.
The Unit Value (UV) is the average value of a single unit of the imported product. It is based on the total value of imports of that product divided by the quantity of imports.
Because AVEs express a tariff as a percentage of the value of goods, UVs are crucial to the process of calculating these AVEs.
There are three approaches, displayed in hierarchical order, for the calculation of a given product UV:
The UV calculation method used by MAcMap depends on the AVE methodology you select. The World Tariff Profile (WTP) method goes systematically through the three approaches listed above and picks the first calculation for which there is sufficient data. That is, if there is sufficient bilateral trade, the first method above will be used. The World Unit Value method goes straight to the third approach listed above. For more information on UV calculation please consult the Methodology submodule.
MAcMap tariff percentages are rounded to two decimal values. Very small nonzero values are therefore shown as 0.00%. If a tariff is reported by a country as zero the application displays 0%. Non-available values, which can occur in those cases where AVEs cannot be calculated (e.g. for technical duties), are denoted as N/A.
In MAcMap, both unit types and rounding rules depend on the type of data and whether the dataset is viewed on-screen or downloaded. The various options are summarized in the table below:
| Variable | Tariff rates | Trade values | ||
| Output support | On screen results | Downloaded files | On screen results and downloaded files | |
| Unit | Percentage | Share | US$ ‘000 | |
| Rounding | Upwards to two decimals | Truncated at five decimals | Upwards to the nearest unit (US$ ‘000) | |
| Smallest value shown | 0.00% which denotes any value smaller than 0.005% | 0.00000 which denotes any value smaller than 0.00001 | 1 which denotes any value between US$1 and US$1000 | |
| Zero (0) | 0% denotes a tariff reported by the country as zero (duty free) | 0 denotes tariff rates reported by the country as zero (duty free) | 0 denotes that no trade was reported between countries | |
| N/A | N/A denotes non-available values, e.g. in case the value cannot be calculated or was not reported | N/A denotes non-available values. This implies values were not reported by countries. | ||
A tariff rate quota is a combination of an import tariff and an import quota in which imports below a specified quantity enter at a lower (or zero) tariff and imports above that quantity enter at a higher tariff.
A tariff rate quota has two parts, the Inside Quota Tariff Rate (IQTR) and the Outside Quota Tariff Rate (OQTR). The threshold quantity between the IQTR and the OQTR is called the quota volume or contingent.
The tariff rate quotas contained in MAcMap are applied tariff rates and the quota volume is an aggregate threshold for all countries and products included in the quota. MAcMap does not have bound tariff rate quota information, nor information on the quota period. Tariff rate quotas are taken into account for AVE calculations (see details in the Methodology). There are a number of ways to administer quotas (see following table).
The application of a reduced tariff rate for a specific quantity of imported goods and a higher tariff for imports above this quantity is known as tariff rate quota. It differs from an import quota, which by contrast, is an explicit limit on the quantity of goods that may be imported.
There are a number of ways to administer quotas.
| Principal methods for administering tariff quotas | |
|---|---|
| Code | Explanation |
| AT | "Applied tariffs": No shares are allocated to importers. Imports are allowed in unlimited quantities at the Inside Quota Tariff Rate (IQTR) or below. |
| FC | "First-come, first-served": No shares are allocated to importers. Imports are permitted entry at the Inside Quota Tariff Rate (IQTR) until such a time as the tariff quota is filled; then the Outside Quota Tariff Rate (OQTR) automatically applies. The physical importation of the good determines the order and hence the applicable tariff. |
| LD | "Licenses on demand": Importers' shares are generally allocated, or licenses issued, in relation to quantities demanded and often prior to the commencement of the period during which the physical importation is to take place. This includes methods involving licenses issued on a first-come, first-served basis and those systems where license requests are reduced pro rata where they exceed available quantities. |
| AU | "Auctioning": Importers' shares are allocated, or licenses issued, largely on the basis of an auctioning or competitive bid system. |
| HI | "Historical importers": Importers' shares are allocated, or licenses issued, principally in relation to past imports of the product concerned. |
| ST | "Imports undertaken by state trading entities": Import shares are allocated entirely or mainly to a state trading entity which imports (or has direct control of imports undertaken by intermediaries) the product concerned. |
| PG | "Producer groups or associations": Import shares are allocated entirely or mainly to a producer group or association which imports the product concerned (or has direct control of imports undertaken by members). |
| MX | "Mixed allocation methods": Administration methods involving a combination of the methods as set out above with no one method being dominant. |
| NS | "Non-specified": Tariff quotas for which no administration method has been notified. |
Non-tariff measures (NTMs) are import/export related regulations that are not in the form of a customs tariff.
NTMs include a wide category of instruments such as: food safety and animal and plant health regulations - otherwise known as sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures; measures relating to the performance, labeling, size/shape, design, function etc. of products - otherwise known as technical barriers to trade (TBT); quotas; anti-competitive measures; import or export licenses; export restrictions; custom surcharges; financial measures; antidumping measures etc. For regulations required by private entities consult private standards.
Information on NTMs available in MAcMap is retrieved from official national sources. The database is continuously updated with new countries being added, whenever possible. To see the latest country covered, please visit Data availability. For more information on the data collection procedure, please visit the Methodology.
Non-tariff measures (NTMs) are a wider concept than non-tariff barriers (NTBs). NTMs include all policy measures other than tariffs that can potentially have an effect on international trade. NTM data presented in MAcMap shows the regulatory environment of a country without any assumptions as to whether a given measure constitutes a barrier to trade or has a protectionist intent.
In MAcMap, NTM regulations refer to the data jointly collected by ITC, UNCTAD and the World Bank and cover rules, procedures and requirements regulating imports and exports, as well as product requirements, e.g. SPS requirements.
The notifications provided by the WTO Member-countries to the WTO Secretariat represent a sub-set of the official regulations shown in MAcMap. The main differences are summarized below.
| ITC-UNCTAD-World Bank data collection | WTO notifications |
|---|---|
| Based on active data collection from numerous national institutions | Based on the notifications submitted by the WTO members to the Secretariat |
| Classified according to the international NTM classification | Classified according to the GATT/WTO agreements |
| Complete coverage of all areas/sectors | Measures referring to areas/sectors where notifications are required under the GATT/WTO agreements |
| All measures in force (stock) | Newly introduced or modified measures (flow) |
| All measures independently of their potential impact on trade | Measures that are deemed potentially trade distorting, e.g. SPS requirements which are stricter than international standards |
| Any country | WTO member states |
After entering your query parameters and executing your download, a “Query is running” notification will appear. Depending on your query, the tool may have to retrieve a large amount of data. Therefore, it may take a while before you will see your query results.
MAcMap will automatically send you an email to inform you when your download query has finished executing. This email will contain a link back to the query result page. Therefore, you can leave the page and switch off your internet access while you are waiting for your results.
Yes, MAcMap allows you to download applied tariffs, non-tariff measures and trade data for multiple years via the Data Download module. Data of the current year may not be available for download due to data protection reasons. See the user guide for step-by-step instructions on how to use the different functionalities in Data Download.
MAcMap allows you to download data on applied tariffs, final bound rates, trade and NTMs. You can currently download up to a maximum of 1,000,000 records per query. Whenever you download data, you will be informed about the number of records you have remaining.
The source of the data must be always acknowledged and cited in the following way: “Market Access Map, International Trade Centre, www.macmap.org, accessed on [dd.mm.yyyy].” The abridged version, to be used below graphs or in body text is “ITC Market Access Map”. Any copying, automated browsing or downloading, redistribution, publication, or commercial exploitation of any materials made available through Market Analysis Tools is prohibited except for the cases explicitly permitted by applicable agreements or by the prior written permission of the International Trade Centre which can be requested by email at marketanalysis@intracen.org.
Please contact us at marketanalysis@intracen.org.
To access more features of the site, register for free in ITC's Market Analysis Tools platform
Register >>